
NEVER STOP EXPLORING
We makes it possible for anyone to actively engage in space-related activities
Our Goals
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Defending Earth
Clean Energy from Space
Communities in Space
Why Space Matters
Join
our PAN
Join
a Chapter
NSS General Fund
Save NEOSM
(Near-Earth Object Surveyor Mission)
FUN FACT
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
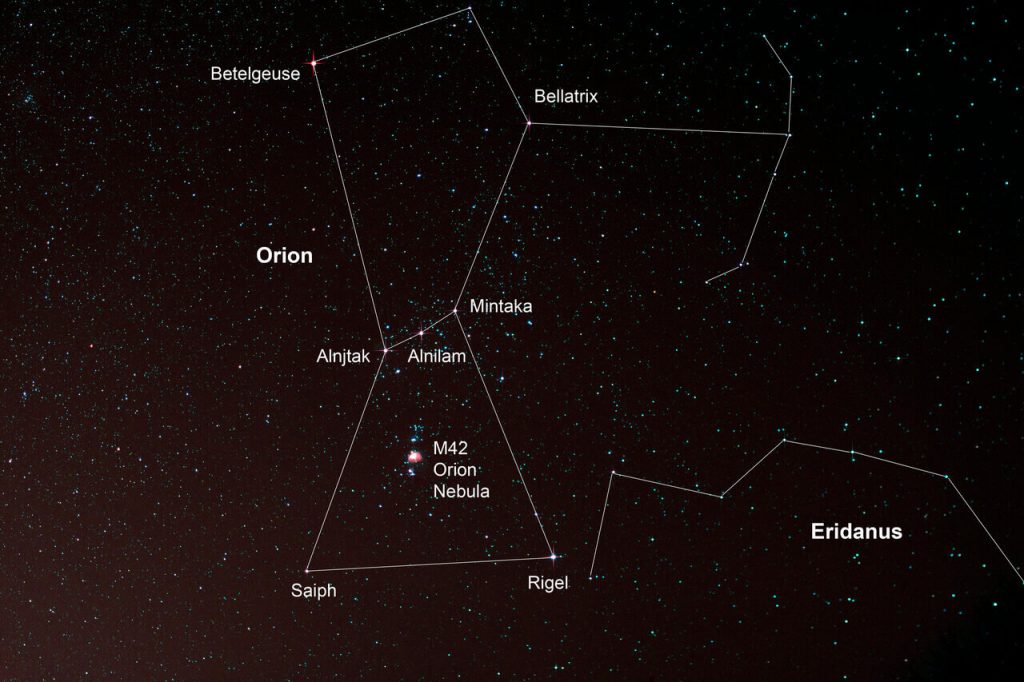
Mintaka
Mintaka is designated as Delta Orionis, and it is the 73 brightest star in the night sky. It is located at around 1,200 light-years / 380 parsecs away from the Sun.
The name Mintaka derives from the Arabic Al Mintakah, which means 'the belt' as it is the first star seen in that portion of the rising constellation Orion. Ancient astrologers considered it of importance as portending good fortune and it is a "steady" star.
Alnilam
Alnilam is located at 1,975 / 600 parsecs away from the Earth. It is the 29th brightest star in the night sky! (the fourth brightest in Orion) Alnilam is a blue supergiant star of spectral type B0 la.
The name Alnilam comes from the Arabic Al Nitham or Al Nathm, meaning “the string of pearls.” The three stars of Orion's belt have a rich history in many culture's folklores. In Chinese mythology, the three stars were referred to as the Weighing Beam.
Alnitak
Alnitak is the brightest class O star in the night sky, shining with an apparent visual magnitude of 1.74. Alnitak is 33 times larger than the Sun, 20 times its diameter and shines 10,000 times its luminosity. This star is estimated to be around six million years-old.
Saiph
Saiph is the 60th brightest star in the night sky and can be observed with the naked eye. The bright star is several times bigger than our Sun. It has around 15.50 solar masses, or 1.550 % the sun's mass, and has around 22.2 solar radii, or 2.220 % the sun's radius.
Saiph, with a temperature of 26,000 Kelvin, is a hot class B (B1) bright supergiant that shines with a sparkling blue-white light.
Rigel
Rigel, also called Beta Orionis, one of the brightest stars in the sky, intrinsically as well as in appearance. A blue-white supergiant in the constellation Orion, Rigel is about 870 light-years from the Sun and is about 47,000 times as luminous. A companion double star, also bluish white, is of the sixth magnitude
Orion
Orion's constellation consists of 81 stars - 7 main stars and a huge red one, named Betelguese. The brightest star in Orion is Rigel; however, Betelgeuse occasionally outshines it. -The three stars that form Orion's Belt are called Alnilam, Mintaka, and Alnitak.
Bellatrix
Bellatrix is a massive star with about 8.6 times the Sun's mass. Bellatrix has 5.75 solar radii – almost six times that of the sun, and it is around 9.211 times brighter. Its name is derived from Latin and it literally means female warrior. Bellatrix is one of the four stars used in celestial navigation.
It's almost 4 times hotter than our sun, more than 5.5 times its size, more than 8.5 times as massive, and more than 6,000 times brighter.
Eridanus
Eridanus is quite a prominent constellation, stretching for 1138 square degrees, being the sixth largest constellation out of the 88 modern constellations in the sky. There are no Messier objects located in Eridanus. There are only two meteor showers associated with Eridanus, the Nu Eridanids and Omicron Eridanids.
M42 Orion Nebula
Popularly called the Orion Nebula, this stellar nursery has been known to many different cultures throughout human history. The nebula is only 1,500 light-years away, making it the closest large star-forming region to Earth and giving it a relatively bright apparent magnitude of 4
The Orion Nebula gets its reddish hue from hydrogen gas, which is energized by radiation from newborn stars. While the red areas are emitting light, the blue-violet regions in the nebula are reflecting radiation from hot, blue-white O-type stars.
Betelgeus
Betelgeuse, also called Alpha Orionis, second brightest star in the constellation Orion, marking the eastern shoulder of the hunter. Its name is derived from the Arabic term bat al-jawzāʾ, which means “the giant's shoulder.” Betelgeuse is one of the most luminous stars in the night sky.
If Betelgeuse does explode, it could become either a neutron star or a black hole. To become a black hole, the material left over by the supernova explosion would have to equal more than 3 solar masses.
Return to the Moon
Enter Your Email for a free copy of ad Astra Article Moon Rockets
If you are not a member of NSS, please consider joining NSS and get access to many excellent articles in ad Astra like Moon Rockets.